碳是生命中不可或缺的元素,具有多種混成方式(sp、sp2、sp3)。比如,石墨和金剛石這兩種碳的同素異形體中,金剛石為sp3混成,形成三維碳原子網絡,而石墨則是sp2混成,形成層狀結構,層與層之間為範德華力相互作用。
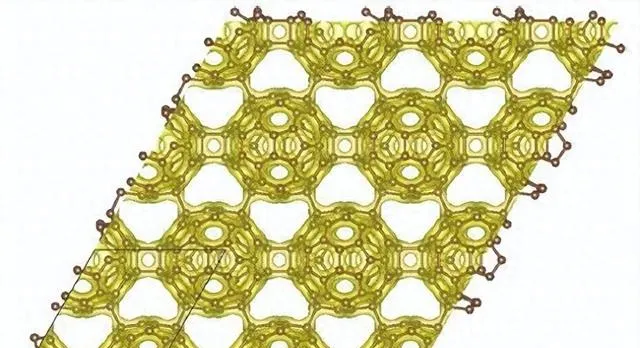
Fig. 1 Two-dimensional projection of the atomic structure of graphullerene together with a high electron density iso-surface.
從石墨中發現石墨烯被認為是凝聚態物理的一項重大突破,然而這些碳同素異形體都不是半導體。C60分子形狀類似足球,由六邊形和五邊形碳原子構成,透過sp2混成與其三個最近的鄰居形成鍵合。
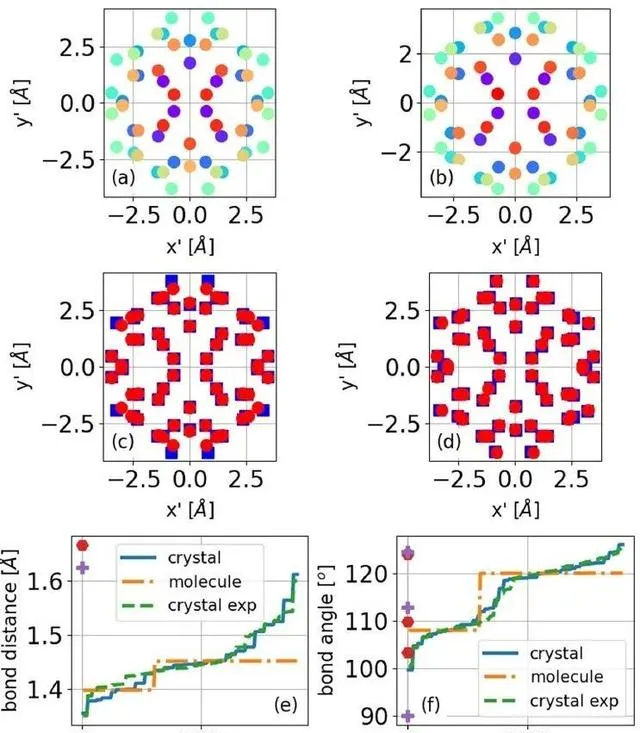
Fig. 2 Analysis of graphullerene structure.
最近的研究合成了Mg與C60分子結合的二維六角形結構(Mg4C60)n。去除Mg後形成了石墨勒烯(Graphullerene),其碳原子同時表現出sp2和sp3混成,暗示了其亞穩定性。Mg原子的摻雜對結構的穩定性影響很大,但Mg原子在穩定結構中的作用及其對材料效能的影響仍有待確定。
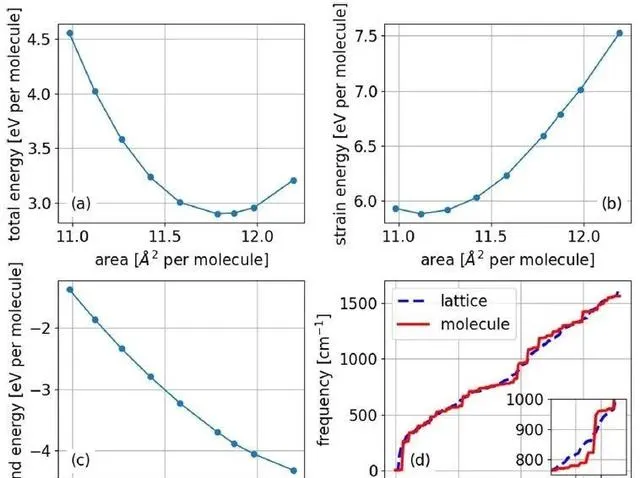
Fig. 3 Energies and frequencies.
來自以色列的本–古賴恩大學材料工程系的Guy Makov教授小組,采用從頭算的方法,研究了石墨勒烯的力學和能量穩定性、原子結構、聲子色散曲線和能帶結構。他們的研究證明了石墨勒烯是一種亞穩態半導體,其結構由受應變的C60分子透過共價鍵與鄰近分子相連構成。
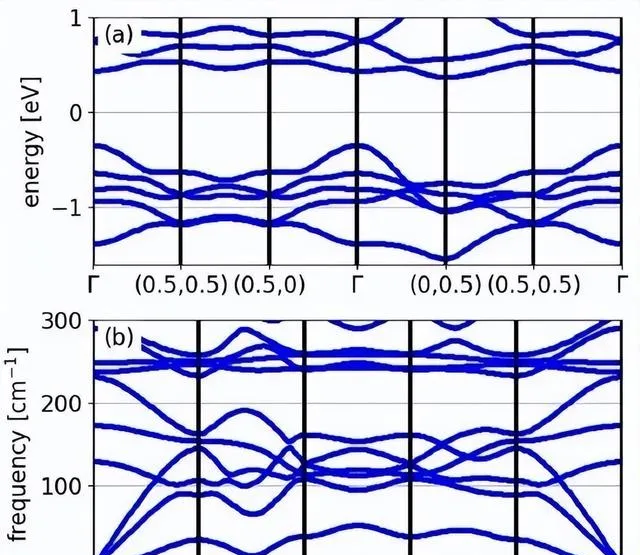
Fig. 4 Band structure and phonon frequencies.
他們還研究測定了石墨勒烯的鍵長和振動譜,並與孤立C60分子進行了對比,發現了石墨勒烯的特征振動訊號。作者揭示了Mg原子的作用,指出加入Mg原子可以使結構的形成能從負值轉為正值,增強結構的能量穩定性,並降低電子帶隙。
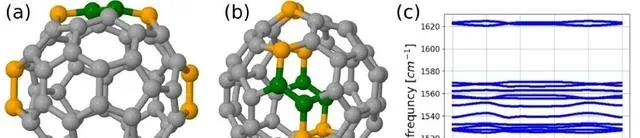
Fig. 5 Phonon modes.
這些發現與實驗觀察一致,為進一步開發這類材料的技術套用和合成路線提供了更堅實的理論基礎。該文近期釋出於 npj Computational Materials 9 : 211 (2023)。
Fig. 6 The electronic density difference between graphullerene with and without Mg atoms.
Editorial Summary
The Symphony of Carbon: A new 2D material graphullerene
Carbon, an essential element in life, exhibits various hybridizations (sp, sp2, sp3) as seen in allotropes like graphite and diamond. Diamond, with sp3 hybridization, forms a three-dimensional carbon network, whereas the sp2 hybridization of graphite creates layered structures held together by van der Waals forces. The discovery of graphene from graphite is a significant breakthrough in condensed matter physics.
However, these carbon allotropes are not semiconductors. C60molecules, resembling soccer balls made of hexagonal and pentagonal carbon atoms, are bonded through sp2 hybridization. Recent studies synthesized a two-dimensional hexagonal structure (Mg4C60)ncombining magnesium and C60 molecules. Upon removing Mg, Graphullerene forms, displaying both sp2 and sp3 hybridizations, suggesting meta-stability. The doping of Mg atoms significantly impacts the structural stability, yet their role in the stabilized structure and influence on material properties remains to be determined.
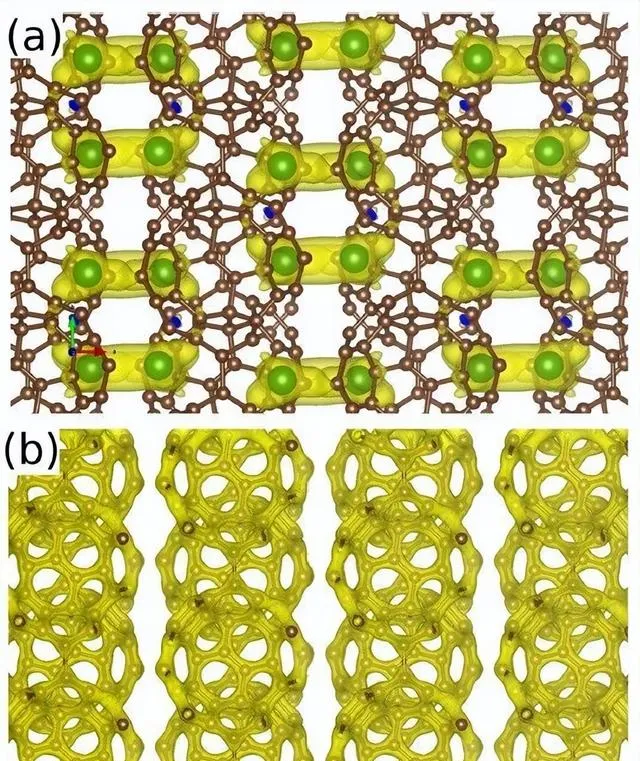
Fig. 7 Electron density of bulk graphullerene.
A group led by Prof. Guy Makov from the Dept. of Materials Engineering, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel, utilized ab initio calculations to study the mechanical and energy stability, atomic structure, phonon dispersion curves, and band structure of graphullerene. Their research confirms graphullerene as a meta-stable semiconductor, structured by strained C60 molecules covalently bonded to neighbors.
They also determined the bond lengths and vibrational spectrum of graphullerene, compared them with isolated C60molecules and identified a characteristic vibrational signature. Moreover, they revealed the role of Mg atoms, noting that their inclusion turns the formation energy from negative to positive, enhancing stability and reducing the electronic band gap. These findings align with experimental observations, laying a solid foundation for further technological applications and synthetic routes of such materials. This article was recently published in npj Computational Materials 9: 211 (2023).
原文Abstract及其轉譯
Structure and properties of graphullerene: a semiconducting two-dimensional C60 Crystal (graphullerene的結構和性質:一種半導體性的二維C60 晶體結構)
Uri Argaman & Guy Makov
Abstract
Graphullerene is a recently discovered, two-dimensional allotrope of carbon formed from C60 molecules. It has been synthesized in the form (C60Mg4)n and subsequently transformed into (C60)n by removal of the Mg atoms. Ab initio calculations are employed to examine the structure and properties of this material. Structurally, graphullerene is composed of strained C60 molecules. Each of these molecules is connected to six neighbors in a hexagonal network with a total of eight chemical bonds. We find this structure to be meta-stable, owing to the strain produced by the covalent bonding of the molecules. However, the inclusion of Mg atoms transforms the cohesion energy from negative to positive values by forming additional C-Mg bonds, creating an energetically stable material. In the absence of Mg, this allotrope is a pure carbon semiconductor with an indirect band gap. Phonon spectrum calculations confirm the dynamical stability of the material and yield its in- and out-of-plane sound velocities. In addition, symmetry breaking of the C60 molecules results in a distribution of bond lengths and creates vibrational modes that serve as a signature of graphullerene.
摘要
Graphullerene是最近發現的一種碳的二維同素異形體,由C60分子組成。它以(C60Mg4)n的形式合成,隨後透過去除鎂原子轉化為(C60)n。我們采用從頭算計算方法來研究這種材料的結構和性質。從結構上看,石墨勒烯(Graphullerene)由受應力的C60分子組成。每個分子都與六個相鄰的分子形成六角形的網絡,總共有八個化學鍵。我們發現這種結構是亞穩定的,這是由於分子間的共價鍵形成的應力導致的。然而,鎂原子的存在透過形成額外的C-Mg鍵將結合能從負值轉化為正值,從而創造出一個在能量上穩定的材料。在沒有鎂的情況下,這種同素異形體是一種純碳半導體,具有間接帶隙。聲子譜確認了材料的動力學穩定性,並得出了其面內和面外聲速。此外,C60分子的對稱性破缺導致鍵長分布的出現,並產生了作為石墨勒烯特征的振動模式。











