
本文 专注 于 Python 字符串总结,试图一文 全面 讲解 Python 常用 字符串操作 ,并且能够一遍就能看懂和学会。
文本目标
零散 的 Python 字符串知识是 没有力量的 。文本的目标你脑子里面长出一颗 Python 字符串的树的 种子 ,让它具有成长的基础属性。当然发芽成长还是自己。
学习方式推荐

推荐使用学习方式使用 jupyter notebook ,为什么呢?很简单 jupyter notebook 可以分段执行,也可以分类。当然你可以使用自己的
pip install jupyterlabjupyter lab # 在 web 环境中链接

当然你也可以在 vscode 使用插件支持 jupyter notebook,在你 vscode 等熟悉的编程器中学习和使用。
定义字符串的方式
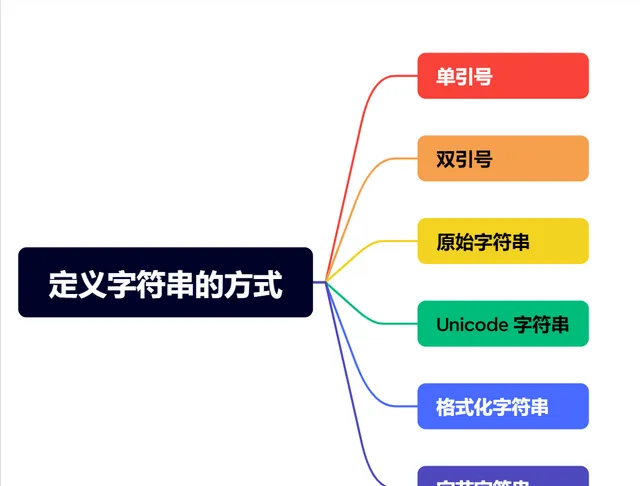
# 1. 单引号字符串str1 = '这是一个字符串'# 2. 双引号字符串str2 = "这是另一个字符串"# 3. 三引号字符串(可以跨多行)str3 = '''这是一个多行字符串可以换行'''# 4. 原始字符串(反斜杠不转义)str4 = r'这是一个原始字符串,包含反斜杠: \n \t'# 5. Unicode 字符串(Python 3 中,字符串默认是 Unicode)str5 = u'这是一个Unicode字符串'# 6. 格式化字符串(插入变量或表达式的值)name = 'Alice'age = 30str6 = f'{name}的年龄是{age}岁'# 7. 字节字符串(用于存储字节数据)str7 = b'hello world'
字符串的基本操作
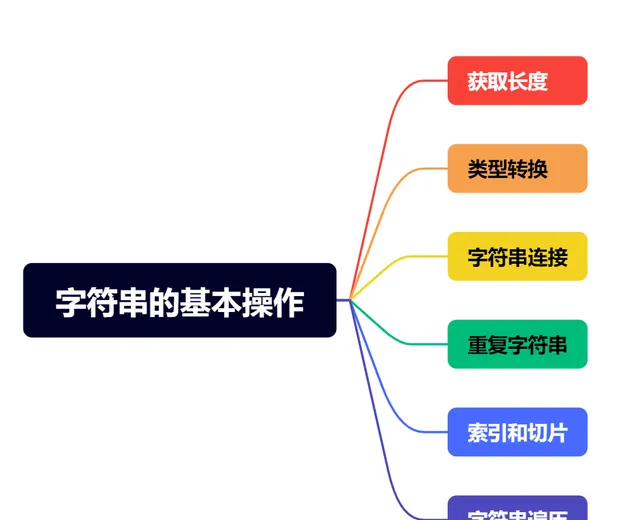
# 原始字符串定义str1 = "Hello"str2 = "World"# 1. 获取长度:len()length = len(str1)# 2. 类型转换:str()num = 123str_num = str(num)# 3. 字符串连接:+str3 = str1 + " " + str2# 4. 重复字符串:*str4 = str1 * 3# 5. 索引和切片: str[i] 和 [str[i:j]]first_char = str1[0] # 索引获取第一个字符slice_str = str1[1:4] # 切片获取子字符串,从索引 1 到 3(不包含 4)# 6. 字符串遍历: for-inprint("遍历字符串结果:")for char in str1: print(char, end=' ')
字符串查找
# 原始字符串定义text = "Hello, welcome to the world of Python. Python is great!"# 查找子字符串:find()substring = "Python"index = text.find(substring)# 子串计数:count() 方法返回子字符串在字符串中出现的次数count = text.count(substring)# 检查开头和结尾:startswith() 方法检查字符串是否以指定的子字符串开始starts = text.startswith("Hello")# endswith() 方法检查字符串是否以指定的子字符串结束ends = text.endswith("great!")# endswith() 方法可以接受一个元组,检查字符串是否以元组中的任意子字符串结尾ends_any = text.endswith(("Python", "great!"))
字符串修改

# 原始字符串定义text = " Hello, welcome to the world of Python. Python is great! "# 1. 大小写转换:lower() 和 upper()lower_text = text.lower() # 将字符串转换为小写upper_text = text.upper() # 将字符串转换为大写# 2. 替换:replace()replaced_text = text.replace("Python", "Java")# 3. 去空格:strip(), lstrip(), rstrip()stripped_text = text.strip() # 去除两端空格lstripped_text = text.lstrip() # 去除左侧空格rstripped_text = text.rstrip() # 去除右侧空格# 4. 字符串拆分:split()words = text.split() # 默认按空白字符拆分# 5. 字符串连接:join()separator = ", "joined_text = separator.join(words) # 用 ', ' 连接列表中的字符串
格式化字符串:

name = "Alice"age = 30# 使用 % 占位符进行格式化formatted_string = "名字: %s, 年龄: %d" % (name, age)formatted_string = "名字: {}, 年龄: {}".format(name, age)formatted_string_index = "名字: {0}, 年龄: {1}".format(name, age)formatted_string_keywords = "名字: {name}, 年龄: {age}".format(name=name, age=age)# 使用 f-string 进行格式化formatted_string = f"名字: {name}, 年龄: {age}"# 支持表达式formatted_string_expr = f"名字: {name.upper()}, 年龄: {age + 5}"# 支持格式化规范formatted_string_float = f"圆周率: {3.14159:.2f}"
字符串检查
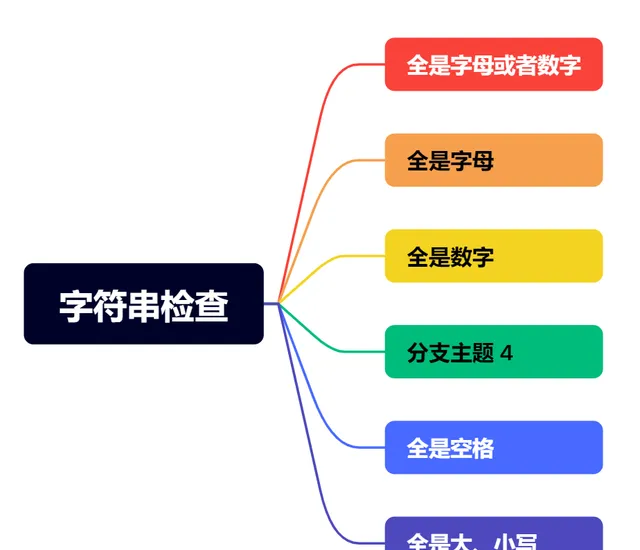
text = " Hello123 "print(f"'{text}' 是否全是字母或数字: {text.isalnum()}") # 输出: Falseprint(f"'{text}' 是否全是字母: {text.isalpha()}") # 输出: Falseprint(f"'{text}' 是否全是数字: {text.isdigit()}") # 输出: Falseprint(f"'{text}' 是否全是空格: {text.isspace()}") # 输出: Falseprint(f"'{text}' 是否全是小写字母: {text.islower()}") # 输出: Falseprint(f"'{text}' 是否全是大写字母: {text.isupper()}") # 输出: False
正则 re 模块

import re# 正则表达式模式pattern = r'\d+' # 匹配一个或多个数字# 1. 编译正则表达式:compile()compiled_pattern = re.compile(pattern)# 2. 查找:search()text = "The number is 12345."match_search = compiled_pattern.search(text)# 3. 匹配:match()text2 = "12345 is the number."match_match = compiled_pattern.match(text2)# 4. 匹配成列表:findall()text3 = "The numbers are 123 and 456."matches_findall = compiled_pattern.findall(text3)# 5. 查找迭代:finditer()matches_finditer = compiled_pattern.finditer(text3)for match in matches_finditer: print(f"位置: {match.start()}, 内容: {match.group()}")# 6. 替换:sub()text4 = "Replace 123 and 456."replaced_text = compiled_pattern.sub('NUMBER', text4)# 7. 拆分:split()text5 = "Split 123 and 456."split_text = compiled_pattern.split(text5)
常用的类库

import stringimport textwrapimport difflibimport unicodedatafrom fuzzywuzzy import fuzzimport regeximport stringcasefrom strsimpy.jaccard import Jaccardfrom pyparsing import Word, alphas, nums, OneOrMore# 1. string 内置模块的属性和方法:print("所有字母: ", string.ascii_letters)print("所有小写字母: ", string.ascii_lowercase)print("所有大写字母: ", string.ascii_uppercase)print("所有数字: ", string.digits)print("所有标点符号: ", string.punctuation)print("所有空白字符: ", string.whitespace)template = string.Template('Hello, $name!')print(template.substitute(name='Alice')) # 输出: Hello, Alice!# 2. textwrap 模块text = "This is a long line of text that we want to wrap to a specified width for better readability."wrapped_text = textwrap.fill(text, width=40)print("textwrap.fill() 结果:")print(wrapped_text)# 3. difflib 模块text1 = "Hello World!"text2 = "Hello Python World!"diff = difflib.ndiff(text1, text2)print("difflib.ndiff() 结果:")print(''.join(diff))# 4. unicodedata 模块char = 'ñ'print(f"字符: {char}")print(f"名称: {unicodedata.name(char)}") # 输出: LATIN SMALL LETTER N WITH TILDEprint(f"类别: {unicodedata.category(char)}") # 输出: Ll (Letter, lowercase)# 5. pyparsing 模块word = Word(alphas)number = Word(nums)sentence = OneOrMore(word | number)result = sentence.parseString("Hello 123 world")print("pyparsing 结果:")print(result) # 输出: ['Hello', '123', 'world']# 6. fuzzywuzzy 模块str1 = "hello world"str2 = "hello"ratio = fuzz.ratio(str1, str2)print(f"fuzzywuzzy.ratio() 相似度: {ratio}") # 输出: 相似度: 60# 7. regex 模块text = "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."pattern = r'\b\w{5}\b'matches = regex.findall(pattern, text)print(f"regex.findall() 匹配的单词: {matches}") # 输出: ['quick', 'brown', 'jumps']# 8. stringcase 模块import stringcasetext = "Hello World"print(f"stringcase.snakecase() 下划线风格: {stringcase.snakecase(text)}") # 输出: hello_worldprint(f"stringcase.uppercase() 大写风格: {stringcase.uppercase(text)}") # 输出: HELLO WORLDprint(f"stringcase.camelcase() 驼峰风格: {stringcase.camelcase(text)}") # 输出: HelloWorld# 9. strsimpy 模块jaccard = Jaccard(2) # 2 表示使用2个字符组成的元组进行比较similarity = jaccard.similarity("night", "nacht")print(similarity) # 输出: 0.14285714285714285
小结
本文系统以 图文 的方式介绍的了 Python 字符串相关内容和实际示例。熟悉一门语言我们快速的建立起知识结构,尤其是当你有多门编程语言的经验。











