EinSum介紹
EinSum (愛因史坦求和)是一個功能強大的算子,能夠簡潔高效地表示出多維算子的乘累加過程,對使用者非常友好。
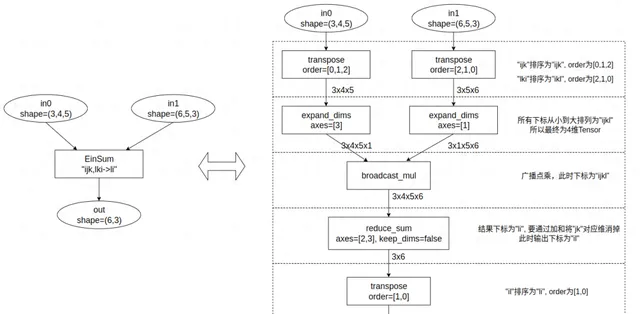
本質上, EinSum是一個算子族,可以表示多種基礎操作,如矩陣乘法、Reduce。EinSum支持任意多的輸入,只要計算中只包含點乘(element-wise)、廣播(broadcast)、歸約求和(reduction sum)都可以使用EinSum來表示。以下給出一種將EinSum計算等價表達的流程:
- 將輸入的維度符號放入一個列表,移除重復元素後按升序排列;
- 對各輸入維度執行轉置操作,確保維度識別元按照升序對齊,實作維度對齊;
- 在缺失的維度上填充1(擴充套件維度),以便與第一步中定義的維度保持一致;
- 對所有輸入執行廣播點乘;
- 對那些不在輸出識別元中的維度執行累加操作;
- 利用轉置操作調整維度順序,使其與輸出識別元的順序一致。
下圖是以 out = EinSum("ijk, lki-> li", in0, in1 ) 為例,根據上述步驟進行等價轉換。
TPU-MLIR轉換
雖然使用上述流程可以完成對EinSum的計算轉換,但如果嚴格按照該流程執行,會帶來大量的Transpose和Reshape操作,這不僅會給TPU-MLIR的LayerGroup功能帶來挑戰,同時也難以顯式地辨識出如矩陣乘法這類操作,從而無法充分利用硬體加速單元。因此,TPU-MLIR並未直接采用上述流程進行轉換。
接下來,我們將詳細介紹EinSum的完整處理過程。
前端介面
以下範例程式碼摘自OnnxConverter.py檔,並附帶了註釋。程式碼整體結構簡潔明了,我們可以看到,轉換函式目前僅支持兩個輸入的常見情況。特別需要註意的是公式的歸一化過程。由於EinSum的運算式可以使用任意非重復字元來表示下標,這雖然提高了可讀性,但也導致 同一操作有多種不同的表示方式。歸一化操作就是將運算式字元重新對映,以字元'a'作為起始。例如,比如 ij,jk->ik 和 dk,kv->dv 都會對映為 ab,bc->ac 。
# https://pytorch.org/docs/1.13/generated/torch.einsum.html?highlight=einsum#torch.einsum def convert_einsum_op(self, onnx_node): assert (onnx_node.op_type == "Einsum") equation = onnx_node.attrs.get("equation").decode() # 公式歸一化 def normalize_equation(equation_c): equation = equation_c new_equation = '' start = 'a' translate_map = {} for s in equation: if s == ' ': continue elif not ((s >= 'a' and s <= 'z') or (s >= 'A' and s <= 'Z')): translate_map[s] = s elif s not in translate_map: translate_map[s] = start start = chr(ord(start) + 1) new_equation += translate_map[s] return new_equation equation = normalize_equation(equation) lhs = self.getOperand(onnx_node.inputs[0]) # # 大多情況下rhs是Weight, self.getOp會先到Weight Map中尋找;如果找不到, # 其會從Mutable Tensor中尋找,然後返回對應的Value。 rhs = self.getOp(onnx_node.inputs[1]) new_op = top.EinsumOp(self.unranked_type, [lhs, rhs], mode=StringAttr.get(equation), # 設定 loc 資訊,方便找到原圖對應算子 loc=self.get_loc("{}_{}".format(onnx_node.name, onnx_node.op_type)), # 將該算子插入到當前的block中 ip=self.mlir.insert_point).output # 將輸出放到Mutable Tensor列表中,供後面算子使用 self.addOperand(onnx_node.name, new_op)
內部轉換
TPU-MLIR目前支持了幾種常見的運算式,並根據不同的算子進行了最佳化轉換。所有的變換最終都利用了硬體的矩陣乘法加速單元,從而實作了對算子的有效加速。以下是部份程式碼片段,該程式碼來自 tpu-mlir/lib/Dialect/Top/Canonicalize/Einsum.cpp ,並在原有基礎上添加了註釋。
struct ConvertEinsum : public OpRewritePattern<EinsumOp> { using OpRewritePattern::OpRewritePattern; LogicalResult matchAndRewrite(EinsumOp op, PatternRewriter &rewriter) const override { // 目前只支持輸入個數為2或者輸入0為Weight的情況 if (op.getInputs().size() != 2 || module::isWeight(op.getInputs()[0])) { llvm_unreachable("Not support now."); // return failure(); } auto none = module::getNoneOp(op); auto mode = op.getMode().str(); auto lhs = op.getInputs()[0]; auto rhs = op.getInputs()[1]; auto lshape = module::getShape(lhs); auto rshape = module::getShape(rhs); std::string lname = module::getName(lhs).str(); std::string rname = module::getName(rhs).str(); std::string name = module::getName(op.getOutput()).str(); std::vector<Value> operands; std::vector<NamedAttribute> attrs; if (mode == "a,b->ab") { // 外積操作: 可看作[a,1]x[1,b]的矩陣乘法操作 // lhs->ReshapeOp(): shape=[a] to shape[a,1] rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(lhs.getDefiningOp()); // auto newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], 1}, module::getElementType(lhs)); auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(lname + "_to2dim")); auto lrsOp = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{lhs}); operands.push_back(lrsOp); // rhs->ReshapeOp(): shape=[b] to shape[1,b] rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); newType = RankedTensorType::get({1, rshape[0]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_to2dim")); auto rrsop = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rhs}); operands.push_back(rrsop); operands.push_back(none); // 用MatMulOp實作[a,1]x[1,b]=[a,b], 並替換原來的EinSum操作 rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(op.getLoc(), op.getType(), operands, attrs); op.replaceAllUsesWith(matmulOp.getOperation()); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else if (mode == "abcd,cde->abe") { // 可以轉換成矩陣乘法[a*b, c*d]x[c*d, e]->[a*b, e]->[a,b,e] // lhs_reshape_rst = [lhs_shape[0] * lhs_shape[1], lhs_shape[2] * lhs_shape[3]] rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(lhs.getDefiningOp()); auto newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0] * lshape[1], lshape[2] * lshape[3]}, module::getElementType(lhs)); auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(lname + "_to2dim")); auto lrsOp = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{lhs}); operands.push_back(lrsOp); newType = RankedTensorType::get({rshape[0] * rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); if (module::isWeight(rhs)) { rhs.setType(newType); operands.push_back(rhs); } else { rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_to2dim")); auto rrsop = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rhs}); operands.push_back(rrsop); } operands.push_back(none); rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0] * lshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(op)); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(name + "_matmul")); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(loc, newType, operands, attrs); auto orsOp = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(op.getLoc(), op.getType(), ValueRange{matmulOp}); op.replaceAllUsesWith(orsOp.getOperation()); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else if (mode == "abcd,bed->abce") { rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); // 轉換過程 // batch matmul does not support broadcast // temporary solution // [h, k, c] -> [1, h, k, c] -> [b, h, k, c] operands.push_back(lhs); RankedTensorType newType; // 右運算元處理 if (auto wOp = dyn_cast<top::WeightOp>(rhs.getDefiningOp())) { // 對於Weight來說,可以將數據復制,解決不支持廣播問題, [b, e, d]->[a, b, e, d] auto storage_type = module::getStorageType(rhs); assert(storage_type.isF32() && "Todo, supoort more weight type"); auto data = wOp.read_as_byte(); uint8_t *dptr; newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); std::vector<float_t> new_filter(newType.getNumElements(), 0); dptr = (uint8_t *)new_filter.data(); // 實際的數據復制過程 for (int32_t i = 0; i < lshape[0]; i++) { auto offset = i * data->size(); memcpy(dptr + offset, data->data(), data->size()); } auto new_op = top::WeightOp::create(op, "folder", new_filter, newType); wOp.replaceAllUsesWith(new_op.getDefiningOp()); operands.push_back(new_op); rewriter.eraseOp(wOp); } else { // 對於普通tensor, 先reshape成[1, b, e, d] 再用tile算子翻倍數據為 [a, b, e, d] // Reshape操作 auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_reshape")); newType = RankedTensorType::get({1, rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); auto rrsop = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rhs}); // Tile操作,各維tile倍數[a,1,1,1] newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_tile")); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("tile", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({lshape[0], 1, 1, 1}))); auto tileOp = rewriter.create<TileOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rrsop}, attrs); attrs.clear(); operands.push_back(tileOp); } operands.push_back(none); // 這裏使用了右運算元轉置的批次矩陣乘法算子, 硬體可直接支持 // [a*b, c, d] * [a*b, e, d]^T -> [a*b, c, e] attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("right_transpose", rewriter.getBoolAttr(true))); rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(op.getLoc(), op.getType(), operands, attrs); op.replaceAllUsesWith(matmulOp.getOperation()); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else if (mode == "abcd,ced->abce") { // dumb implementation // 轉置lhs [a, b, c, d] -> [a, c, b, d] // trans_shape = [lhs_shape[0], lhs_shape[2], lhs_shape[1], lhs_shape[3]] rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(lhs.getDefiningOp()); auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(lname + "_trans")); auto newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[2], lshape[1], lshape[3]}, module::getElementType(lhs)); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("order", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({0, 2, 1, 3}))); auto tranOp = rewriter.create<PermuteOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{lhs}, attrs); attrs.clear(); operands.push_back(tranOp); // 復制或Tile lhs: [c,e,d] -> [a,c,e,d] rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); if (auto wOp = dyn_cast<top::WeightOp>(rhs.getDefiningOp())) { // Weight翻倍數據 auto storage_type = module::getStorageType(rhs); assert(storage_type.isF32() && "Todo, supoort more weight type"); auto data = wOp.read_as_byte(); uint8_t *dptr; newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); std::vector<float_t> new_filter(newType.getNumElements(), 0); dptr = (uint8_t *)new_filter.data(); for (int32_t i = 0; i < lshape[0]; i++) { auto offset = i * data->size(); memcpy(dptr + offset, data->data(), data->size()); } auto new_op = top::WeightOp::create(op, "folder", new_filter, newType); wOp.replaceAllUsesWith(new_op.getDefiningOp()); operands.push_back(new_op); rewriter.eraseOp(wOp); } else { // rehshape + tile: [c,e,d] -reshape->[1,c,e,d]-tile->[a,c,e,d] loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_reshape")); newType = RankedTensorType::get({1, rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); auto rrsop = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rhs}); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_tile")); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("tile", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({lshape[0], 1, 1, 1}))); newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); auto tileOp = rewriter.create<TileOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rrsop}, attrs); attrs.clear(); operands.push_back(tileOp); } operands.push_back(none); // 右運算元帶轉置批次矩陣乘法:[a*c, b, d] * [a*c, e, d]^T -> [a*c, b, e]->[a, c, b, e] newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[2], lshape[1], rshape[1]}, module::getElementType(op)); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("right_transpose", rewriter.getBoolAttr(true))); rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(name + "_matmul")); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(loc, newType, operands, attrs); attrs.clear(); // [b, w, h, k] -> [b, h, w, k] attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("order", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({0, 2, 1, 3}))); auto tranBackOp = rewriter.create<PermuteOp>(op.getLoc(), op.getType(), ValueRange{matmulOp}, attrs); op.replaceAllUsesWith(tranBackOp.getOperation()); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else if (mode == "abcd,abed->abce" || mode == "abcd,abde->abce") { // lhs(abcd) * rhs(abed)^T -> abce // lhs(abcd) * rhs(abde) -> abce auto newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[1], lshape[2], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(op)); if (mode == "abcd,abde->abce"){ newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[1], lshape[2], rshape[3]}, module::getElementType(op)); } rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); operands.push_back(lhs); operands.push_back(rhs); operands.push_back(none); if (mode == "abcd,abed->abce"){ //rhs(abed)^T attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("right_transpose", rewriter.getBoolAttr(true))); } auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(name)); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(loc, newType, operands, attrs); op.replaceAllUsesWith(matmulOp.getOperation()); attrs.clear(); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else if (mode == "abcd,cde->abce"){ // lhs : // abcd -> acbd(pemute) // rhs : // cde -> 1cde(reshape) // acde -> acde(tile) // matmul: // lhs(acbd) * rhs(acde) = result(acbe) // result: // acbe -> abce(pemute) // success! rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(lhs.getDefiningOp()); auto loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(lname + "_trans")); auto newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[2], lshape[1], lshape[3]}, module::getElementType(lhs)); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("order", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({0, 2, 1, 3}))); auto tranOp = rewriter.create<PermuteOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{lhs}, attrs); attrs.clear(); operands.push_back(tranOp); rewriter.setInsertionPointAfter(rhs.getDefiningOp()); if (auto wOp = dyn_cast<top::WeightOp>(rhs.getDefiningOp())) { auto data = wOp.read_as_byte(); uint8_t *dptr; newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); std::vector<float_t> new_filter(newType.getNumElements(), 0); dptr = (uint8_t *)new_filter.data(); for (int32_t i = 0; i < lshape[0]; i++) { auto offset = i * data->size(); memcpy(dptr + offset, data->data(), data->size()); } auto new_op = top::WeightOp::create(op, "folder", new_filter, newType); wOp.replaceAllUsesWith(new_op.getDefiningOp()); operands.push_back(new_op); rewriter.eraseOp(wOp); } else { loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_reshape")); newType = RankedTensorType::get({1, rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); auto rrsop = rewriter.create<ReshapeOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rhs}); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(rname + "_tile")); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("tile", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({lshape[0], 1, 1, 1}))); newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], rshape[0], rshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(rhs)); auto tileOp = rewriter.create<TileOp>(loc, newType, ValueRange{rrsop}, attrs); attrs.clear(); operands.push_back(tileOp); } operands.push_back(none); newType = RankedTensorType::get({lshape[0], lshape[2], lshape[1], rshape[2]}, module::getElementType(op)); rewriter.setInsertionPoint(op); loc = NameLoc::get(rewriter.getStringAttr(name + "_matmul")); auto matmulOp = rewriter.create<MatMulOp>(loc, newType, operands, attrs); attrs.clear(); attrs.push_back(rewriter.getNamedAttr("order", rewriter.getI64ArrayAttr({0, 2, 1, 3}))); auto tranBackOp = rewriter.create<PermuteOp>(op.getLoc(), op.getType(), ValueRange{matmulOp}, attrs); op.replaceAllUsesWith(tranBackOp.getOperation()); rewriter.eraseOp(op); } else { llvm_unreachable("Einsum not support this mode now"); } return success(); }
總結
TPU-MLIR對EinSum的實作雖然不完全,但已經足夠實用,能滿足目前常見網路的需求。透過Converter直接運算式規範化,降低了編譯器最佳化或模式分析的復雜性。在算子分析時,我們不僅需要在計算上實作等價變換,還需充分了解實際硬體的特性。針對不同硬體架構及其對算子的支持情況,需具體分析以找到最佳實作方法。此外,我們可以看到在工程實踐中,人們更註重實用性和效率,在實作上不必追求完備,是要覆蓋實際套用場景即可。EinSum的轉換還有改進空間,我們也歡迎社群提出寶貴的建議並貢獻程式碼。











