* 仅供医学专业人士阅读参考

8张表格,快速理清!
撰文丨 杨凤娟
近日,在山东省青岛世界博览城盛大召开的 第二十九次皮肤性病学术年会(CSD 2024)上,中国医学科学院皮肤病医院陆前进教授 详细介绍了2023年中国皮肤科基础研究的科研成果。

图1:陆前进教授作精彩报告
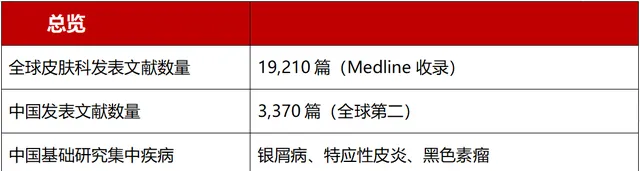
陆前进教授首先分享到,全球皮肤科发表了19,210篇Medline收录的文献,其中中国发表了3,370篇,数量位居世界第二。中国的基础研究主要集中在 银屑病、特应性皮炎和黑色素瘤 三大疾病上,热点方向包括微生物组学、细胞多组学、代谢重编程和神经免疫。
表1:2023年中国皮肤科主要科研进展总览
1、皮肤生物学——伤口愈合与毛囊再生
表2:2023年皮肤生物学主要科研进展

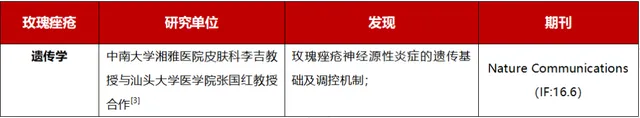
2、玫瑰痤疮
表3:2023年玫瑰痤疮主要科研进展
3、银屑病
表4:2023年银屑病主要科研进展

4、红斑狼疮
表5:2023年红斑狼疮主要科研进展

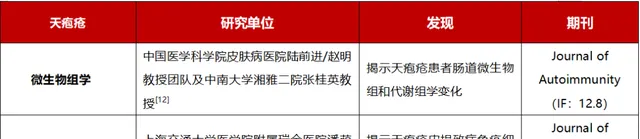
5、天疱疮、类天疱疮
表6:2023年天疱疮、类天疱疮主要科研进展
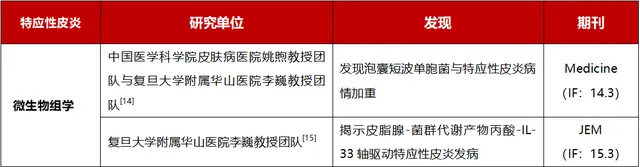
6、特应性皮炎
表7:2023年特应性皮炎主要科研进展
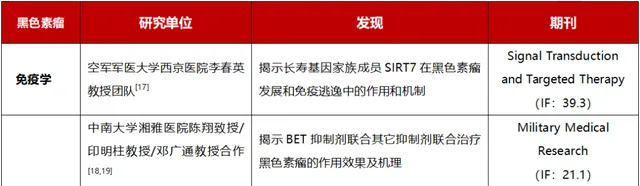
7、黑色素瘤
表8:2023年黑色素瘤主要科研进展
陆前进教授展望了中国皮肤科科研的发展,指出随着基础研究的深入,越来越多的新细胞亚群、新发病机制和新药物靶点被发现,为全面解析皮肤病的发病机制提供理论基础,并为未来的诊疗策略提供新方向。
专家简介

中国医学科学院皮肤病医院教授、博士生导师、主任医师
北京协和医学院长聘教授
中国医学科学院学部委员
中华医学会皮肤性病学分会第十五届主任委员
中国免疫学会皮肤免疫分会主任委员
中国医师协会皮肤科分会副会长
国际皮肤科学会联盟常务理事
中华皮肤科杂志总编辑
Clinical Immunology 杂志副主编
Exp Dermatol 杂志副主编
更多皮肤前沿内容
快来「 医生站网 页版 」瞧一瞧 👇
或点击阅读原文
精彩资讯等你来
参考文献:
[1] Yin J, Shi D, Sun Y.et al. IRF7 and CTSS are pivotal for cutaneous wound healing and may serve as therapeutic targets[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 8(1): 1–4.
[ 2] Wang G, Sweren E, Andrews W.et al. Commensal microbiome promotes hair follicle regeneration by inducing keratinocyte HIF-1α signaling and glutamine metabolism[J]. Science Advances, American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2023, 9(1): eabo7555.
[3 ] Deng Z, Chen M, Zhao Z.et al. Whole genome sequencing identifies genetic variants associated with neurogenic inflammation in rosacea[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 3958.
[4 ] Zhao Q, Yu J, Zhou H.et al. Intestinal dysbiosis exacerbates the pathogenesis of psoriasis-like phenotype through changes in fatty acid metabolism[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 8(1): 1–18.
[5 ] Cai X, Han M, Lou F.et al. Tenascin C+ papillary fibroblasts facilitate neuro-immune interaction in a mouse model of psoriasis[J]. Nature Communications, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 14(1): 2004.
[6 ] Chen J, Bai Y, Xue K.et al. CREB1-driven CXCR4hi neutrophils promote skin inflammation in mouse models and human patients[J]. Nature Communications, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 14(1): 5894.
[7 ] Lu J, Zhong X, Guo C.et al. TLR7-MyD88-DC-CXCL16 axis results neutrophil activation to elicit inflammatory response in pustular psoriasis[J]. Cell Death & Disease, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 14(5): 1–13.
[8 ] Li Q, Shao S, Zhu Z.et al. An IGFBP7hi endothelial cell subset drives T cell extravasation in psoriasis via endothelial glycocalyx degradation[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, American Society for Clinical Investigation, 2023, 133(9).
[9 ] Chen C, Yi X, Liu P.et al. CD147 Facilitates the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis through Glycolysis and pK9me3 Modification in Keratinocytes[J]. Research, American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2023, 6: 0167.
[10 ] Tian J, Zhang D, Yao X.et al. Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, 2023, 82(3): 351–356.
[11 ] Zhao M, Feng D, Hu L.et al. 3D genome alterations in T cells associated with disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, 2023, 82(2): 226–234.
[12 ] Guo Z, Yiu N, Hu Z.et al. Alterations of fecal microbiome and metabolome in pemphigus patients[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2023, 141: 103108.
[13 ] Xu C, Zhang T, Wang H.et al. Integrative single-cell analysis reveals distinct adaptive immune signatures in the cutaneous lesions of pemphigus[J]. Journal of Autoimmunity, 2024, 142: 103128.
[14 ] Liu X, Xu B, Xu X.et al. Attenuation of allergen-specific immunotherapy for atopic dermatitis by ectopic colonization of Brevundimonas vesicularis in the intestine[J]. Cell Reports Medicine, Elsevier, 2023, 4(12).
[15 ] Qiu Z, Zhu Z, Liu X.et al. A dysregulated sebum–microbial metabolite–IL-33 axis initiates skin inflammation in atopic dermatitis[J]. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2022, 219(10): e20212397.
[16 ] Tian J, Zhang D, Yang Y.et al. Global epidemiology of atopic dermatitis: a comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study[J]. British Journal of Dermatology, 2024, 190(1): 55–61.
[17 ] Yi X, Wang H, Yang Y.et al. SIRT7 orchestrates melanoma progression by simultaneously promoting cell survival and immune evasion via UPR activation[J]. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 8(1): 1–17.
[18 ] Meng Y, Sun H-Y, He Y.et al. BET inhibitors potentiate melanoma ferroptosis and immunotherapy through AKR1C2 inhibition[J]. Military Medical Research, 2023, 10(1): 61.
[19 ] Zeng F, Li Y, Meng Y.et al. BET inhibitors synergize with sunitinib in melanoma through GDF15 suppression[J]. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, Nature Publishing Group, 2023, 55(2): 364–376.
[20 ] Liu N, Chen L, Yan M.et al. Eubacterium rectale Improves the Efficacy of Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy in Melanoma via l-Serine-Mediated NK Cell Activation[J]. Research, American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2023, 6: 0127.
本文审核:陆前进教授
责任编辑: 刘思思
*"医学界"力求所发表内容专业、可靠,但不对内容的准确性做出承诺;请相关各方在采用或以此作为决策依据时另行核查。











