
分享興趣,傳播快樂,增長見聞,留下美好!
親愛的您,這裏是LearningYard新學苑。
今天小編帶你學習多內容決策知識,
歡迎您的存取!
Share interest, spread happiness,
increase knowledge, and leave beautiful.
Dear, this is the LearingYard Academy!
Today, the editor brings the 「Knowledge of multi-attribute decision-making」.
Welcome to visit!

VIOKR方法最早由前南斯拉夫的教授Opricavic在二十世紀90年代末提出的。該方法是一種在理想點法的基礎上對最終排序進行了改進的方法,透過采用折衷的思想對多內容決策問題的研究進行最佳化。VIKOR方法的基本原理的第一步同TOPSIS方法的基本原理相類似,同樣為獲取正理想解以及負理想解,接下來進行折衷排序,依據為評價值與理想方案的距離。此方法的核心為不僅將群體效益值進行最大化處理,而且將個體遺憾值進行最小化處理,還能將決策者的個人偏好加到其中,因此決策者才能最終接受所求得的妥協解。在對方案的評價過程中,VIKOR方法裏妥協折衷排序的思想利用了Lmetricp-聚合函數,該函數的測度描述如下:
The VIOKR method was first proposed by Professor Opricavic from former Yugoslavia in the late 1990s. This method is an improvement on the final ranking based on the ideal point method, which optimizes the research of multi-attribute decision-making problems by adopting a compromise approach. The first step in the basic principle of the VIKOR method is similar to that of the TOPSIS method, which is to obtain both positive and negative ideal solutions. Next, a compromise ranking is performed based on the distance between the evaluation value and the ideal solution. The core of this method is not only to maximize the group benefit value, but also to minimize the individual regret value, and to incorporate the decision-maker's personal preferences into it, so that the decision-maker can ultimately accept the compromise solution obtained. In the evaluation process of the scheme, the VIKOR method utilizes the Lmetric aggregation function with the compromise ranking idea, and the measurement description of this function is as follows:
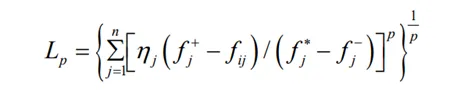
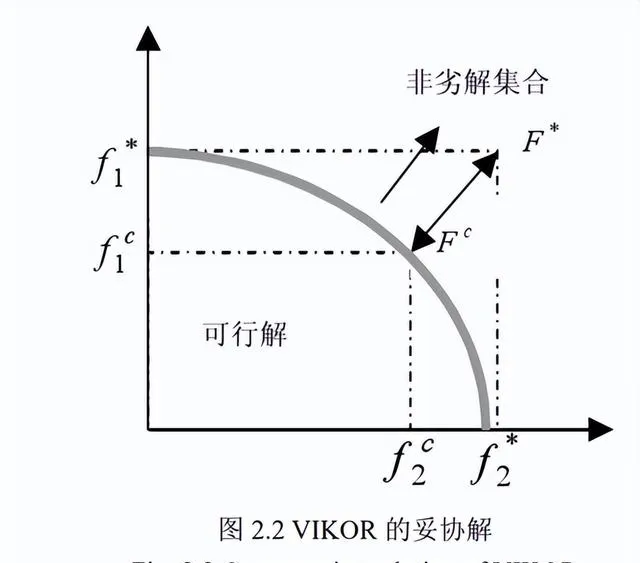
VIKOR方法的妥協解圖例為下圖所示:
The compromise solution legend of the VIKOR method is shown in the following figure:
相關計算步驟如下所示:
步驟一:確定正負理想解
The relevant calculation steps are as follows:
Step 1: Determine positive and negative ideal solutions
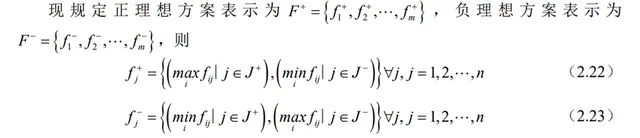
第二步:計算各方案的群體效益值和個體遺憾值
Step 2: Calculate the group benefit value and individual regret value of each plan
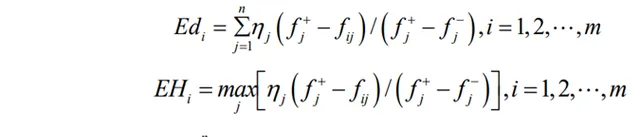
步驟三:計算各方案的最終 VIKOR 值Qi 。
Step 3: Calculate the final VIKOR value Qi for each scheme.
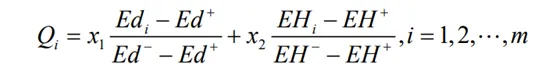
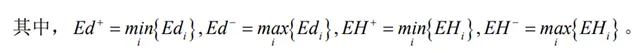
其中Edi和EHi均為成本型變量,即變量的取值結果越小越好。Qi為第i個方案的綜合評價值,Qi的取值越小方案越優。X1、X2Î [0,1]為決策系數,用來表示決策者的個人偏好度。若X1>X2時就表示決策者更加偏好於群體的觀點,認為群體觀點更重要;若X1<X2時就表示決策者更加偏好於個體遺憾度,認為個體觀點更重要;若X1=X2= 0.5時表示決策者不存在明顯的偏好情況。
Edi and EHi are both cost type variables, meaning that the smaller the value of the variable, the better. Qi is the comprehensive evaluation value of the i-th scheme, and the smaller the value of Qi, the better the scheme. X1, X2 Î [0,1] are decision coefficients used to represent the individual preferences of decision-makers. If X1>X2, it indicates that decision-makers are more inclined towards the perspective of the group and believe that the group perspective is more important; If X1<X2, it indicates that decision-makers are more inclined towards individual regret and believe that individual opinions are more important; If X1=X2=0.5, it indicates that the decision-maker does not have a clear preference situation.
第四步:分別根據所計算出的群體效益值Edi、個體遺憾值EHi和VIKOR值Qi對備選方案進行排序,得到三組序列排序表。
其中VIKOR的約束條件主要有兩個:閾值和決策可靠度。
閾值公式為:
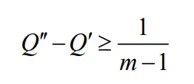
Step 4: Sort the alternative solutions based on the calculated group benefit value Edi, individual regret value EHi, and VIKOR value Qi, and obtain three sets of sequence sorting tables.
There are two main constraints for VIKOR: threshold and decision reliability.
The threshold formula is:
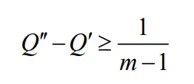
當有多個方案進行排序時,要將排在第一方案的 Q 值與排在第二、第三等方案的Q 值一一進行比較,看是否滿足約束條件 1。該約束條件是為保證決策方案間具有較強 的顯著性。
When there are multiple options for sorting, compare the Q values of the first option with those of the second, third, and other options one by one to see if constraint 1 is met. This constraint is to ensure strong saliency between decision options.
今天的分享就到這裏了。
如果您對今天的文章有獨特的想法,
歡迎給我們留言,
讓我們相約明天,
祝您今天過得開心快樂!
That's all for today's sharing.
If you have a unique idea about the article,
please leave us a message,
and let us meet tomorrow.
I wish you a nice day!
參考資料:百度百科、百度轉譯
參考文獻:劉大林. 基於VIKOR方法的電商環境下供應商評價研究[D]. 沈陽工業大學, 2021.











