
分享興趣,傳播快樂,增長見聞,留下美好!
親愛的您,這裏是LearningYard新學苑。
今天小編給您帶來
【周周記:數學建模學習(28)】
歡迎您的存取!
Share interest, spread happiness, increase knowledge, leave a beautiful!
Dear, this is LearningYard New Academy.
Today, the editor brings you
"Weekly Diary: Learning Mathematical Modeling (28)"
Welcome to your visit!
主成分分析法基本原理與推導
Basic principles and derivation of principal component analysis
一.PCA的基本原理
One. The basic principle of PCA
PCA的目標是在盡量保留原始數據集特征的前提下,降低數據的維度。這透過找到數據中變異數最大的方向來實作,這些方向稱為主成分。
The goal of PCA is to reduce the dimensionality of the data while preserving the characteristics of the original dataset as much as possible. This is achieved by finding the directions with the greatest variance in the data, which are called principal components.
1.數據標準化:由於特征的因次和數值範圍可能不同,首先需要對數據進行標準化處理,使得每個特征的均值為0,標準差為1。
1. Data standardization: Since the dimensions and numerical ranges of features may be different, the data needs to be normalized first, so that the mean value of each feature is 0 and the standard deviation is 1.
2. 共變異數矩陣:計算標準化後數據的共變異數矩陣,以確定特征之間的關系。
2. Covariance Matrix: Calculate the covariance matrix of the normalized data to determine the relationship between features.
3.特征值和特征向量:計算共變異數矩陣的特征值和對應的特征向量。特征值表示特征向量方向上的變異數量,而特征向量表示主成分的方向。
3. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors: Calculate the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix and the corresponding eigenvectors. The eigenvalues represent the amount of variance in the direction of the eigenvector, while the eigenvector represents the direction of the principal component.
4.選擇主成分:根據特征值的大小,選擇最重要的幾個特征向量,這些向量是原始數據集變異數最大的方向。
4. Select principal components: According to the magnitude of the eigenvalues, select the most important eigenvectors, which are the direction of the largest variance of the original data set.
5.構造新的特征空間:將原始數據投影到選定的主成分上,得到降維後的數據表示。
5. Construct a new feature space: project the original data onto the selected principal components to obtain the reduced data representation.
二.PCA的推導過程
Two. Derivation process of PCA
假設我們有 m 個 n 維的數據點,構成矩陣 X∈Rm×n。
Suppose we have m n-dimensional data points that make up the matrix X∈Rm×n.
1.中心化數據: Xcentered=X−μ
1. Centralized data: Xcentered=X−μ
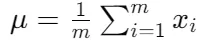
這是每個特征的均值。
There is the mean of each feature.
2.構建共變異數矩陣
2. Construct a covariance matrix
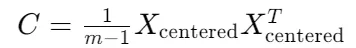
這裏使用 m−1作為歸一化因子是為了得到無偏估計。
M−1 is used here as the normalization factor to obtain an unbiased estimate.
3.求解共變異數矩陣的特征值和特征向量
3. Solve the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the covariance matrix
求解 C 的特征值 λ λ 和對應的特征向量 v,滿足: Cv=λv特征向量表示主成分的方向,特征值表示在該方向上的變異數量。
Solve the eigenvalues λλ of C and the corresponding eigenvectors v, satisfying: Cv=λv eigenvectors represent the direction of the principal components, and the eigenvalues denote the variance in that direction.
4.選擇主成分
4. Select principal components
按照特征值從大到小的順序選擇 k 個最大的特征值對應的特征向量,構成矩陣 P: P=[v1,v2,...,vk]。其中,vi是第 i個最大特征值對應的特征向量。
Select the eigenvectors corresponding to k largest eigenvalues in the order of eigenvalues from large to small to form the matrix P: P=[v1,v2,...,vk].where vi is the eigenvector corresponding to the i-th largest eigenvalue.
5.構造新的特征空間
5. Construct a new feature space
將原始數據投影到選定的主成分上,得到降維後的數據:
Project the original data onto the selected principal components to obtain the reduced data:
Y=XcenteredP
Y=XcenteredP
Y 是降維後的數據,其列是新的主成分,它們是線性獨立的,並且包含了原始數據集中最主要的變異數資訊。
Y is the dimensionality reduction data, and its columns are new principal components that are linearly independent and contain the most important variance information from the original dataset.
三.數學推導
Three. Mathematical derivation
為了找到變異數最大的方向,我們可以使用拉格朗日乘數法來求解最大化問題。我們希望找到方向向量 w(其中 w是單位向量,即 wTw=1),使得數據在 w w 方向上的投影的變異數最大。
To find the direction with the largest variance, we can use the Lagrange multiplier method to solve the maximization problem. We want to find the direction vector w (where w is the unit vector, i.e., wTw=1) so that the variance of the projection of the data in the direction of ww is maximized.
變異數的計算公式為:
The variance is calculated as:
為了最大化變異數,我們需要最大化 wTCw,其中 C是共變異數矩陣。
這是一個典型的特征值問題,可以透過求解以下最佳化問題得到:
To maximize the variance, we need to maximize wTCw, where C is the covariance matrix. This is a typical eigenvalue problem that can be obtained by solving the following optimization problem:
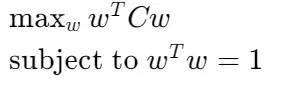
透過拉格朗日乘數法,我們可以得到 C 的特征值和特征向量。特征向量 v 就是最大化變異數的單位方向向量,而對應的特征值 λ 就是最大化的變異數值。
With the Lagrange multiplier method, we can get the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of C. The eigenvector v is the unit direction vector that maximizes the variance, and the corresponding eigenvalue λ is the maximized variance value.
四.總結
Four. summary
PCA透過最大化數據在新方向上的變異數來找到主成分,這些主成分是原始數據集中最重要的特征。透過選擇最大的幾個特征值對應的特征向量,我們可以將數據投影到這些主成分上,從而實作降維。這種方法在數據預處理、特征提取和視覺化中非常有用。
PCA finds the principal components by maximizing the variance of the data in the new direction, which are the most important features in the original dataset. By selecting the eigenvectors corresponding to the largest eigenvalues, we can project the data onto these principal components, thereby reducing the dimensionality. This approach is useful in data preprocessing, feature extraction, and visualization.
今天的分享就到這裏了。
如果您對今天的文章有獨特的看法,
歡迎給我們留言,
讓我們相約明天,
祝您今天過得開心!
That's all for today's share.
If you have a unique view of today's article,
Please leave us a message,
Let's meet tomorrow,
Have a nice day!
本文由LearningYard新學苑原創,如有侵權,請聯系刪除。
參考資料:嗶哩嗶哩
轉譯:Kimi











