
分享興趣,傳播快樂,增長見聞,留下美好。
親愛的您,這裏是LearningYard學苑!
今天小編為大家帶來【偏好資訊不完全時的不確定決策】一文的擴充套件和結論部份。
歡迎您的存取!
Share interest, spread happiness, increase knowledge, and leave beautiful.
Dear, this is the LearingYard Academy!
Today, the editor brings the extensions and conclusion of the article "Decision making under uncertainty when preference information is incomplete".
Welcome to visit!
1 內容摘要(Content summary)
今天小編將從「思維導圖、精讀內容、知識補充」三個板塊,解讀分享【偏好資訊不完全時的不確定決策】一文的擴充套件和結論部份。
Today, the editor will interpret and share the extensions and conclusion of the article "Decision making under uncertainty when preference information is incomplete" from the three ps of "mind map, intensive reading content, and knowledge supplement".
2 思維導圖(Mind mapping)

3 精讀內容(Intensive reading content)
文章的第五節為擴充套件部份,在這一節作者討論了前文中框架的兩個擴充套件。第一個擴充套件為考慮決策者在被調查的隨機事件中的偏好情況與期望效用框架的公理不一致。第二個擴充套件為幾乎隨機優勢及三種不同風格的介紹,並講解了整合它們的方法。
The fifth p of the article is the extension part. In this p, the author discusses two extensions of the previous framework. The first extension is to consider situations where the decision maker's preferences in the random event under investigation are inconsistent with the axioms of the expected utility framework. The second expansion is an introduction to the advantages of almost randomness and three different styles, and explains how to integrate them.

第一個擴充套件為對引出錯誤的解釋,解釋了為什麽決策者所作的比較可能與預期效用理論不一致,可能因為決策者的實際偏好不滿足預期效用公理。作者給出的方法框架可以辨識並對這些不一致進行處理。
The first extends to an explanation of elicitation errors, explaining why comparisons made by the decision-maker may be inconsistent with expected utility theory, perhaps because the decision-maker's actual preferences do not satisfy the expected utility axiom. The methodological framework presented by the authors can identify and deal with these inconsistencies.

後續作者描述了三種容易解釋的不同類別的錯誤,分別是比較時考慮雜訊破壞預期效用評估、假設錯誤存在於對結果值的感知中和決策者選擇錯誤時的情況。
Subsequent authors describe three different types of errors that are easily explained, namely when accounting for noise in comparisons corrupts expected utility assessments, when assumptions error resides in the perception of outcome values, and when decision makers make wrong choices.
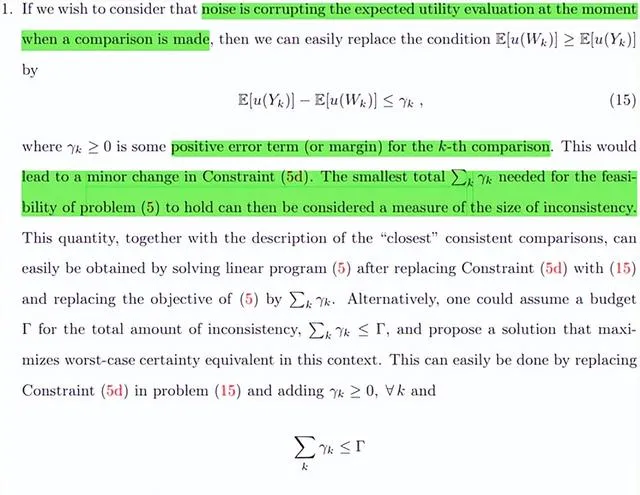
第二個擴充套件為幾乎隨機優勢,講了透過假設附加結構來降低隨機優勢約束的嚴重性的想法的一些具體實踐,分為三個例項,前兩個對效用函數做了假設,與本文框架較為接近,第三個與第一節中的方法較為接近。作者提出了擴充套件結果以分別實作這三種情況中所提議的松弛的方法,分別為Meyer松弛、Leshno Levy松弛和Lizyayev松弛。
The second extension, Almost Random Advantage, talks about some concrete practice of the idea of reducing the severity of the stochastic advantage constraint by assuming additional structure. It is divided into three examples. The first two make assumptions about the utility function and are closer to the framework of this article. The third one is closer to the method in the first p. The authors propose methods to extend the results to implement the proposed relaxations in these three cases, respectively Meyer relaxation, Leshno Levy relaxation and Lizyayev relaxation.

結論部份,作者總結了文章的主要內容,即提出了處理關於效用函數的不完全資訊的簡單方法,研究了目標的三種不同表述以及三種不同類別的效用函數集。文章還有很多創新點,如提出了魯棒確定性等效公式、涉及S形效用和審慎效用的模型等。
In the conclusion part, the author summarizes the main content of the article, that is, a simple method for processing incomplete information about utility functions is proposed, and three different formulations of goals and three different types of utility function sets are studied. The article also has many innovative points, such as proposing a robust deterministic equivalent formula, a model involving S-shaped utility and prudent utility, etc.

文章所提出的框架為後續的進一步研究留下了很多空間,比如如何從決策者那裏獲得有關風險偏好的準確資訊等。
The framework proposed in the article leaves a lot of room for further research, such as how to obtain accurate information about risk preferences from decision makers.
4 知識補充(Knowledge supplement)
什麽是預期效用假說?
What is the expected utility hypothesis?
預期效用假說認為微觀經濟學、博弈論、決策論中,在風險情況下,個人所做出的選擇是追求某一數量的預期價值的最大化,該假說用於解釋保險中的期望值。
The expected utility hypothesis holds that in microeconomics, game theory, and decision theory, under risk situations, the choice an individual makes is to pursue the maximization of a certain amount of expected value. This hypothesis is used to explain the expected value in insurance.
關於風險行為的預期效用假說,它本質上假設單個決策者擁有定義在某些結果集合上的馮諾依曼摩根斯頓效用函數或馮諾依曼摩根斯頓效用指數。當單個決策者面臨關於這些結果的各種可選擇預期時,他將選擇使預期值最大的預期。
Regarding the expected utility hypothesis of risky behavior, it essentially assumes that a single decision maker has a von Neumann Morgenstern utility function or a von Neumann Morgenstern utility index defined on some set of outcomes. When an individual decision maker is faced with alternative expectations about these outcomes, he will choose the expectation that maximizes the expected value.
由於結果可以表示為財富水平、多維商品集、消費的時間流量或非數碼結果,故這個理論可用於多方面,例如不確定性經濟學的理論研究,不確定條件下最優貿易、投資等套用研究。
Since outcomes can be expressed as wealth levels, multidimensional sets of goods, time flows of consumption, or non-numerical outcomes, this theory can be used in many ways. For example, theoretical research on uncertainty economics and applied research on optimal trade and investment under uncertain conditions.
今天的分享就到這裏了。
如果您對今天的文章有獨特的想法,
歡迎給我們留言,
讓我們相約明天,
祝您今天過得開心快樂!
That's all for today's sharing.
If you have a unique idea about the article,
please leave us a message,
and let us meet tomorrow.
I wish you a nice day!
參考資料:
轉譯:Google轉譯
文字:
預期效用假說 - MBA智庫百科 (mbalib.com)
參考文獻:
Benjamin Armbruster, Erick Delage. Decision making under uncertainty when preference information is incomplete [J]. Management science, 2015, 61(1): 111-128.
版權說明:
本文由LearningYard學苑整理並行出,如有侵權請後台留言溝通。
文案I姜瘋雨火
排版I姜瘋雨火
稽核IGoldfish











