肺癌大咖談丨將新研究成果融入實踐,應對EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC治療中的挑戰
EGFR 20 號外顯子插入(exon20 insertion mutation,Ex20ins)突變發生率居 EGFR 基因突變第 3 位,僅次於 19 號外顯子缺失突變和 21 號外顯子 L858R 點突變。本文介紹 ASCO Daily News 釋出的一篇廣東省人民醫院吳一龍教授和林嘉欣教授關於EGFR Ex20ins突變非小細胞肺癌(NSCLC)治療的文章。

要點:
EGFR突變是NSCLC中關鍵的致癌驅動變異之一。高達90%的EGFR突變是外顯子19缺失和外顯子21L858R置換。約10%的EGFR突變NSCLC可檢測到Ex20ins,這是第三大最常見的啟用EGFR突變亞型[1]。與經典EGFR變體類似,Ex20ins在女性、從不吸煙或輕度吸煙者以及腺癌組織學型別患者中最常見。
EGFR Ex20ins由C-螺旋(AA761-766)和緊鄰C-螺旋的環(AA767-775)出現的1-4個胺基酸(AA)插入組成。在已鑒定的60多種獨特的EGFR Ex20ins亞型中,大多數位於C螺旋後的環內[2]。這種復雜的突變譜導致了EGFR Ex20ins突變腫瘤的生物學差異和對EGFR抑制劑的不同敏感性。例如,EGFRA763_Y764insFQEA對第一代EGFR-TKI敏感,而環內突變亞型則對EGFR-TKI不敏感[3]。為了盡可能檢測出所有可靶向治療的EGFR Ex20ins,指導臨床實踐中的治療決策,中國指南和國際指南建議進行下一代測序(NGS)檢測[4]。
不同於敏感EGFR突變患者在EGFR-TKI研發問世後實作了臨床治療效果顯著改善,EGFR Ex20ins患者的預後較差[5,6]。近年來,專門針對EGFR Ex20ins的新型靶向藥物取得了重大進展,例如mobocertinib、amivantamab和舒沃替尼。然而,這些新藥的療效數據無法媲美高效靶向療法(例如奧希替尼)。在這裏,我們對EGFR Ex20ins晚期NSCLC患者的分子檢測和治療管理的最新發現和即將面臨的挑戰進行概述(圖)[7]。
圖. 治療EGFR Ex20ins晚期NSCLC的一般方法和當前治療策略
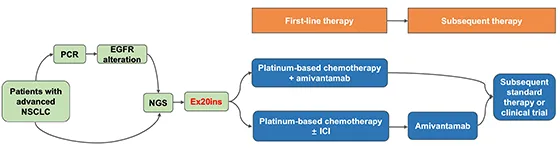
*NCCN指南2024 V5版推薦。
EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC的治療策略
一線治療
由於現有EGFR-TKI的臨床獲益有限, 鉑類雙藥化療 仍然是一線治療中推薦用於攜帶EGFR Ex20ins的患者的最有效治療方法[6]。
值得註意的是,靶向EGFR和MET的新型雙特異性抗體amivantamab在III期PAPILLON試驗中顯示出令人鼓舞的結果。對於未經治療的EGFR Ex20ins患者,與單純化療相比,amivantamab聯合化療可改善無進展生存期(HR=0.40;95%CI: 0.30-0.53)和客觀緩解率(73%;95%CI: 1.32-1.68])[8]。鑒於其優越的療效,FDA批準 amivantamab聯合化療 的一線治療適應癥[9]。
在現實世界中,化療的療效始終優於現有的EGFR-TKI,但在化療中添加免疫檢查點抑制劑(ICI)幾乎沒有臨床獲益[10,11]。到目前為止,ICI聯合化療的獲益以及ICI在EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC治療中的最佳位置都沒有明確結論。但值得註意的是, 無論PD-L1表達水平如何,單藥ICI都不應作為EGFR Ex20ins患者的一線療法 [12]。
二線及後續治療
根據I期CHRYSALIS試驗的結果,amivantamab被批準用於初始化療期間或之後疾病進展的EGFR Ex20ins晚期NSCLC患者[13,14]。後續治療選擇包括標準全身治療或納入臨床試驗。
EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC的新型靶向藥物
表. EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC靶向治療的主要前瞻性臨床試驗
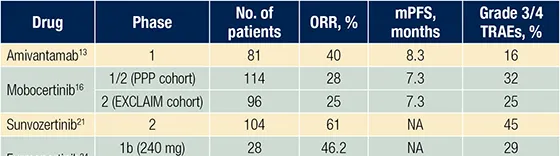
Eblast/網站的摘要:在NSCLC領域,專門針對EGFR Ex20ins的新型靶向藥物取得了重大進展,然而,這些新型藥物的療效數據無法與高效靶向療法相媲美,因此產生了在臨床實踐中使用哪種藥物的問題。
結論和觀點
隨著選擇性靶向EGFR Ex20ins新型TKI的研發以及amivantamab獲批EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC治療的適應癥,EGFR Ex20ins突變NSCLC治療的前景令人興奮。然而,未來仍存在新的挑戰。新藥物的探索應尋求在提高療效和降低毒性的基礎上進行改進。一線治療存在巨大未被滿足的需求,亟需有效的治療策略。未來的臨床試驗也可能考慮比較Ex20ins特異性TKI vs amivantamab聯合化療。最後,確定最佳治療順序對於改善患者的長期預後至關重要。總之,仍需要進一步研究針對該患者群體的治療方法。
參考文獻
1.Arcila ME, Nafa K, Chaft JE, et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(2):220-229.
2.Riess JW, Gandara DR, Frampton GM, et al. Diverse EGFR exon 20 insertions and co-occurring molecular alterations identified by comprehensive genomic profiling of NSCLC.J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(10):1560-1568.
3.Naidoo J, Sima CS, Rodriguez K, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions in advanced lung adenocarcinomas: Clinical outcomes and response to erlotinib.Cancer. 2015;121(18):3212-3220.
4.Viteri S, Minchom A, Bazhenova L, et al. Frequency, underdiagnosis, and heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion mutations using real-world genomic datasets.Mol Oncol. 2023;17(2):230-237.
5.Remon J, Hendriks LEL, Cardona AF, Besse B. EGFR exon 20 insertions in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a new history begins.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020;90:102105.
6.Bazhenova L, Minchom A, Viteri S, et al. Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and common EGFR mutations.Lung Cancer. 2021;162:154-161.
7.National Comprehensive Cancer Network.NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 5.2024. Published April 23. 2024. Accessed May 2, 2024.
8.Zhou C, Tang K-J, Cho BC, et al; PAPILLON Investigators. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(22):2039-2051.
9.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves amivantamab-vmjw for EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small cell lung cancer indications. Published March 1, 2024. Accessed May 1, 2024.
10.Yang G, Li J, Xu H, et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients: Molecular heterogeneity and treatment outcome from nationwide real-world study. Lung Cancer. 2020;145:186-194.
11.Choudhury NJ, Schoenfeld AJ, Flynn J, et al. Response to standard therapies and comprehensive genomic analysis for patients with lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR exon 20 insertions. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(10):2920-2927.
12.Jaiyesimi IA, Leighl NB, Ismaila N, et al. Therapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer with driver alterations: ASCO living guideline, version 2023.3. J Clin Oncol. 2024;42(11):e1-e22.
13.Park K, Haura EB, Leighl NB, et al. Amivantamab in EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: initial results from the CHRYSALIS phase I study. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(30):3391-3402.
14.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to amivantamab-vmjw for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Published May 21, 2021. Accessed May 2, 2024.
15.Gonzalvez F, Vincent S, Baker TE, et al. Mobocertinib (TAK-788): a targeted inhibitor of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutants in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021;11(7):1672-1687.
16.Zhou C, Ramalingam SS, Kim TM, et al. Treatment outcomes and safety of mobocertinib in platinum-pretreated patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 1/2 open-label nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7(12):e214761.
17.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA grants accelerated approval to mobocertinib for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Published September 16, 2021. Accessed May 2, 2024.
18.J ä nne PA, Wang B-C, Cho BC, et al. 507O EXCLAIM-2: phase III trial of first-line (1L) mobocertinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in patients (pts) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion (ex20ins)+ locally advanced/metastatic NSCLC.?Ann Oncol. 2023;34:4s (suppl; abstr 507O).
19.Takeda. Takeda Provides Update on EXKIVITY (mobocertinib). Published October 2, 2023. Accessed May 6, 2024.
20.Wang M, Yang JC-H, Mitchell PL, et al. Sunvozertinib, a selective EGFR inhibitor for previously treated non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(7):1676-1689.
21.Wang M, Fan Y, Sun M, et al. Sunvozertinib for patients in China with platinum-pretreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation (WU-KONG6): single-arm, open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2024;12(3):217-224.
22.Dizal Pharma. Dizal’s sunvozertinib approved in China NMPA with potential best-in- class therapy in NSCLC with EGFR exon20ins mutations. Published August 23, 2023. Accessed May 2, 2024.
23.Yang JC-H, Wang M, Chiu C-H, et al. 1325P Sunvozertinib as first-line treatment in NSCLC patients with EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations. Ann Oncol. 2023;34:2s (suppl; abstr 1325P).
24.Han B, Zhou C, Zheng W, et al. OA03.04 a phase 1b study of furmonertinib, an oral, brain penetrant, selective EGFR inhibitor, in patients with advanced NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Thorac Oncol. 2023;18(11):S49.
25.Piotrowska Z, Tan DS-W, Smit EF, et al. Safety, tolerability, and antitumor activity of zipalertinib among patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(26):4218-4225.
26.Nguyen D, Shum E, Baik CS, et al. Emerging phase I data of BLU-451 in advanced NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:16s (suppl; abstr 9064).











